Modern Challenges in Sending Large Files (And How to Overcome Them)
Approximately 402.74 million terabytes of data are created each day on the internet. That includes videos, photos, software, books, and every form of content you can imagine. Think of data as the building blocks in the world of bits.
That data then needs to move to various destinations, and that’s where the challenge occurs. If you ask a stranger to send a large file to you over the internet, many people will draw a blank. Large file transfer is still a fundamental challenge for many of us. So, how do you send large files over the Internet? Why is it still so difficult today?
Let’s talk about that.
The Ever-Scaling Internet: What is a Large File in 2024?
A large digital file is different today than it was a few years ago. As the internet (and our devices) have improved over the years, we’ve steadily raised the floor and ceiling on data transfer needs. In other words, our definition of what qualifies as a large digital file keeps changing as technology improves.
For the purpose of this article, we’ll define large files as anything ranging from 500MB to 2GB in size — and above.
Challenges in Sending Large Files
Sending a large digital file — without the appropriate software — isn’t as easy as clicking send on an email. There are several technical bottlenecks that you must overcome. And no, bandwidth alone isn’t the golden answer.
This is a common misconception about file sharing. The notion that increased network bandwidth accelerates file transfers is only partially true, at best. That’s because network throughput (how much data you can send at once) is contingent on many factors, including:
- Distance: How far is the data traveling?
- Network Congestion: How “busy” is the network?
- Storage: How fast is the file storage’s read/write ability?
- Connection: What is the speed of the slowest connected point (including ports, cables, etc.)?
- Bandwidth activity and allocation: How will the underlying protocol prioritize your bandwidth to ensure the large files move fast?
- Public Internet: How will outside network speeds and infrastructure impact your file transfer?
- Software: Is your selected software (Dropbox, FTP, etc.) able to send this size file?
It helps to think of bandwidth like a highway. Yes, the width of the highway (bandwidth) will impact traffic speed — but so will other factors such as traffic, distance, the windy nature of the road, and so on.
Take distance as an example.
Large file transfers over long distances are prone to delays and potential failures. That’s why high-frequency traders on Wall Street gain an advantage by being geographically closer to servers. It’s a multi-billion-dollar race to send and receive market data faster than other trading firms.
The closer traders are to the data, the greater their advantage. The same is true for your business as you seek to transfer large digital files, but proximity isn’t always possible.
Now, let’s invert these problems to find the solution.
Large File Transfer: A Tech Guide
There are two common protocols for moving data:
- Transmission control protocol (TCP)
- User datagram protocol (UDP)
Here’s how they work:
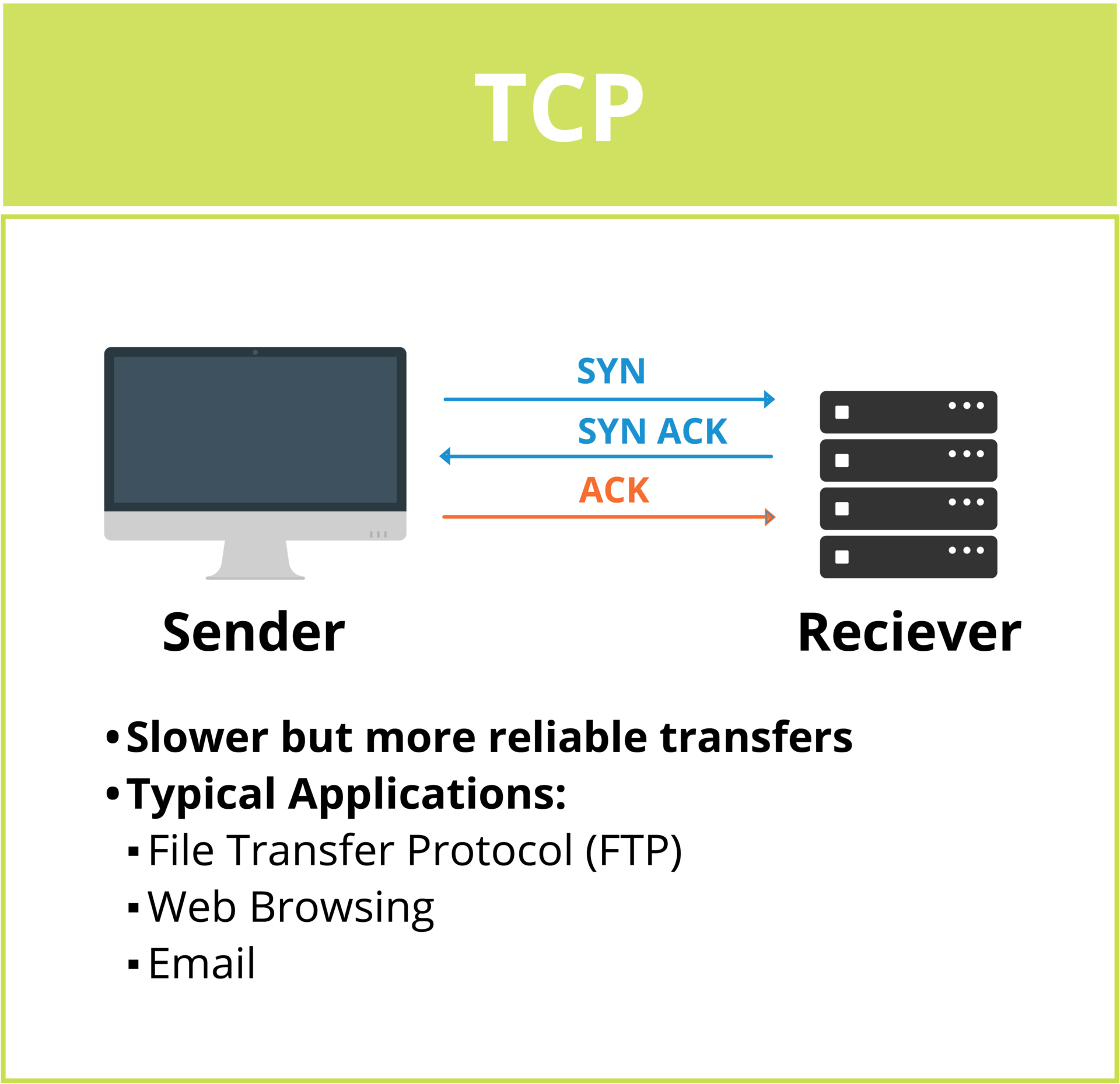
Transmission Control Protocol
TCP works by breaking data into packets, sending each packet to the destination, and waiting for confirmation before sending the next packet. It then reassembles those packets in the correct order. TCP transfers ensure reliable communication by checking for errors and retransmitting lost or corrupted data.
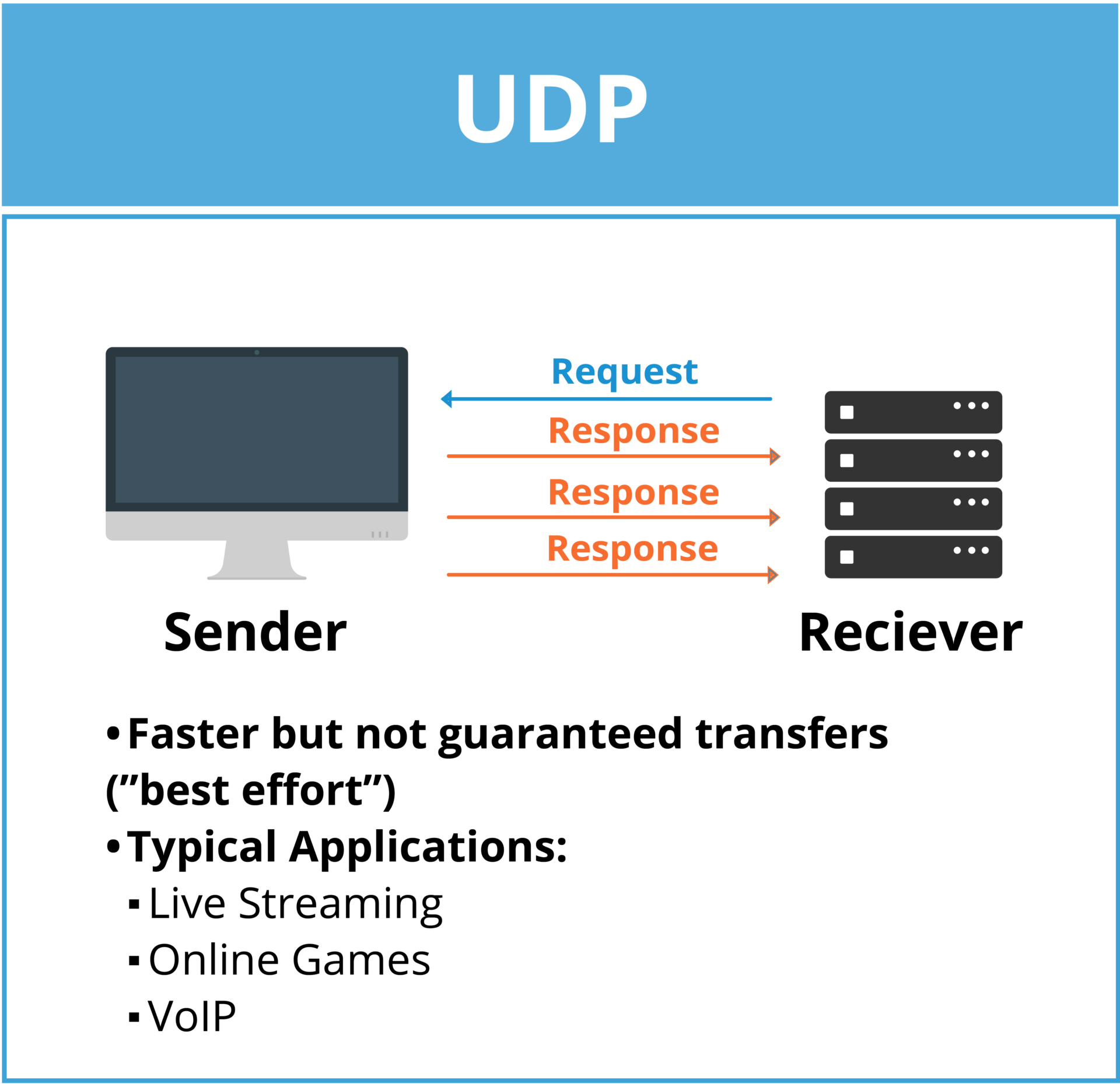
User Datagram Protocol
UDP is a lightweight communication protocol that allows data to be sent quickly between devices and a network but doesn’t confirm they are sent correctly. It transmits messages (called datagrams), providing a fast and efficient way to send information that is useful for video streaming.
| PROTOCOLS | PRO | CON |
| TCP | Reliable data transfer with flow control and error detection; ensures data is received in the correct order | Higher overhead and latency; slower than UDP |
| UDP | Extremely fast with low latency; supports broadcasting and multicasting | No guarantee of delivery; prone to packet loss and unreliability |
In today’s world of massive files and data sets, the right protocol combines the best of both.
Merging the benefits of TCP and UDP transfers offers a powerful solution for sending large files. TCP is known for its reliability, ensuring data arrives in the correct order and without loss, while UDP is valued for its speed, minimizing delivery delays. By integrating the strengths of both protocols, one can achieve high-speed data transfers with the dependability of TCP.
Finding the Right File Sending Service
It’s one thing to understand the underlying tech. It’s another to select the right large file transfer service for your business.
On a practical level, most people send large files today through one of several online service providers, but files are still being sent on a drive via courier services or even by mail. Since you’re reading this article, we’ll assume standard USPS isn’t your preferred option.
So, how do you select the right file online sharing provider? There are four essential characteristics to look for in a large file-sharing solution:
If you’re in the market for a large file transfer tool, consider Media Shuttle by Signiant.
Media Shuttle Solves the Problem of Sending Large Files
Media Shuttle is the easiest and most reliable way for people to send any size of file, anywhere, fast. With Media Shuttle, you can securely access and share media assets from any storage, on-premises or in the cloud. With over 1,000,000 global end-users, it is the de facto industry standard for person-initiated file transfers.
With its intuitive interface and accelerated file transfer technology, Media Shuttle allows users to transfer even the largest media assets with ease, regardless of file size or location. Leverage cloud-native technology to eliminate the frustrations of slow transfers and network limitations.
Media Shuttle also includes robust security features and detailed tracking, ensuring peace of mind and full visibility throughout the entire transfer process.
Here are six key features and capabilities of Media Shuttle:
- Accelerated File Transfers: Media Shuttle uses advanced acceleration technology to enable fast and efficient transfers of large files, sending large files up to 100x faster than standard tools.
- Signiant UDP: Signiant’s proprietary acceleration technology combines the speed of UDP with the reliability of TCP by implementing advanced flow control, congestion control, and reliability mechanisms to ensure high-speed, efficient, and dependable data transfer.
- User-Friendly Interface: Designed with simplicity in mind, Media Shuttle’s intuitive interface allows users of all technical levels to send and receive files easily without the need for IT assistance.
- Flexible Storage Options: Media Shuttle offers storage independence for on-premises and cloud storage, giving organizations the flexibility to choose their preferred storage solutions.
- Comprehensive Security: Media Shuttle provides enterprise-grade security features, including end-to-end encryption and secure authentication, ensuring that all file transfers are protected against unauthorized access.
- Scalability: Media Shuttle is built to scale with your organization, handling any number of users and file sizes, making it suitable for businesses of all sizes.